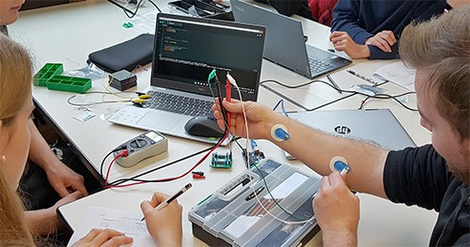
Peter Osypka Institute of Medical Engineering
Research
Research in medical engineering at Hochschule Offenburg focuses on improving medical technologies and procedures. Through innovative projects and state-of-the-art labs, the University develops solutions that can be directly implemented in clinical practice. These efforts help to improve patient-oriented treatments and make the healthcare system more efficient. Our strong links with industry make it possible to respond quickly to current challenges in healthcare, benefiting both local and global healthcare. In addition, the Peter Osypka Institute of Medical Engineering conducts basic research, for example to better understand processes in the human brain.
Fields of research
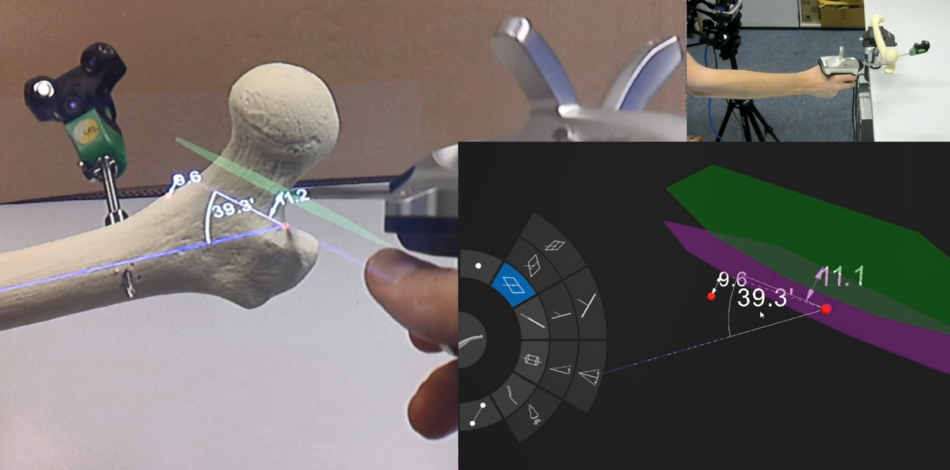
The scientific work in the field of surgical navigation and augmented reality focuses on the development of new technologies to support computer-assisted surgical interventions. Both commercially available navigation systems and self-developed devices are used. The focus is also on the use of augmented reality goggles to provide the surgeon with location-accurate overlays directly in the surgical site. The exact calibration of the cameras and AR glasses used is of crucial importance in these applications.
![[Translate to English:] Eletrostimulation und Ablation [Translate to English:] Elektrostimulation und Ablation](/fileadmin/_processed_/b/4/csm_Bild_Forschung_E_Stim_Ablat_59969817b1.jpg)
The aim of the research and development focus on electrostimulation and ablation is the continuous improvement of diagnostics and therapy of heart diseases.
Cooperation with maximum care institutions such as the MediClin Heart Center Lahr/Baden and the University Hospital of the Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich enables us to conduct interdisciplinary basic and clinical application research and to develop new methods and technologies.
With the aim of increasing the effectiveness of education and training of medical and medical technology staff, company employees and students of medical technology, we are developing didactic solutions for teaching and learning materials for cardiac electrotherapy in cooperation with the Freiburg University of Education.
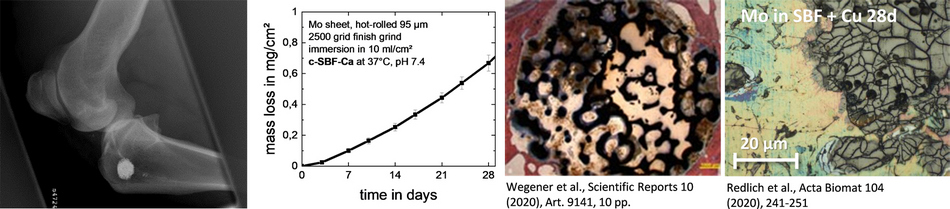
The new research field of medical engineering materials is currently being established at Offenburg University of Applied Sciences. The focus is on materials and manufacturing processes in medical engineering with an emphasis on metallic materials, biodegradable metals and additive manufacturing methods. A corresponding research laboratory is also being set up and will be available for laboratory tests, project work and final theses as well as for research projects.
![[Translate to English:] NeuroAkustik [Translate to English:] NeuroAkustik](/fileadmin/_processed_/a/4/csm_csm_Cochlea_Grafik_MedEl_900_36a2ba2fa8_44ec4299f0.jpg)
![[Translate to English:] NeuroAkustik [Translate to English:] NeuroAkustik](/fileadmin/_processed_/a/3/csm_Abbildung_2_Copyright_Offenburg_University_49da9e7a8f.jpg)
![[Translate to English:] NeuroAkustik [Translate to English:] NeuroAkustik](/fileadmin/_processed_/c/2/csm_Messaufbau_Copyright_Offenburg_University_8f2b447c38.jpg)
Research in the field of neuroacoustics focuses on a deeper understanding of the human auditory system - also in interaction with other sensory organs. The aim is to further improve diagnostics and thearpy of hearing loss, for example with hearing aids or cochlear implants. Methods of signal processing, technical and audiological acoustics, electrical engineering and computer science are used.
Research in NeuroScience is currently focused on the development of new intelligent neuroprosthetic approaches, primarily for the hand. This involves the use of 3-D computer-aided design (CAD), multi-material polymer printing, finite element method (FEM), deep learning and augmented reality methods.
![[Translate to English:] NeuroScience [Translate to English:] NeuroScience](/fileadmin/_processed_/d/4/csm_NeuroScience_1_Copyright_Offenburg_University_cfe514b262.jpg)
![[Translate to English:] NeuroScience [Translate to English:] NeuroScience](/fileadmin/_processed_/a/e/csm_NeuroScience_2_high_resolution_Copyright_Offenburg_University_94d1d5dfef.jpg)
![[Translate to English:] NeuroScience [Translate to English:] NeuroScience](/fileadmin/_processed_/7/9/csm_NeuroScience_3_Copyright_Offenburg_University_56c3a89e2c.jpg)
Current Projects
| Title | Optimierung der zeitlichen Verarbeitung bei CI-Hörgeräte-Versorgung, Teil 3 |
| Short Name | OCI III |
| Short Description | Das Nachfolgeprojekt von OCI II widmet sich der Entwicklung geeigneter Anpassungsmethoden zur Referenz-ITD-Reduktion bei bimodaler CI-Versorgung sowie deren Auswirkungen auf die Schalllokalisation. Es handelt sich um ein Projekt vom Typ IIT. Das Projekt ist mit einer kooperativen Promotion an der HS Offenburg verbunden. Die wissenschaftliche Fragestellung und die Methodenauswahl basieren auf eigenen Vorarbeiten, die an der Hochschule Offenburg in Kooperation mit der Uniklinik Freiburg erarbeitet und publiziert wurden. Ergebnisse, die innerhalb der Projekts erzielt werden, werden auf nationalen und internationalen Tagungen präsentiert und in einschlägigen nationalen und internationalen Fachjournalen publiziert. Journalartikel aus den Projekten OCI1 und OCI2 (Auszug): Zirn, S., Angermeier, J., Arndt, S., Aschendorff, A., & Wesarg, T. (2019). Reducing the device delay mismatch can improve sound localization in bimodal cochlear implant/hearing-aid users. Trends in Hearing, 23, https://doi.org/10.1177/2331216519843876. Angermeier, J., Hemmert, W., & Zirn, S. (2021). Sound Localization Bias and Error in Bimodal Listeners Improve Instantaneously When the Device Delay Mismatch Is Reduced. Trends in Hearing, 25, https://doi.org/10.1177/23312165211016165. |
| Year Of Acquisition | 2022 |
| Start Date | 2022-04-01 |
| End Date | 2025-03-01 |
| Project Managers | Zirn, Stefan, Prof. Dr. |
| Faculties | EMI |
| Institution | POIM |
| Funder Kind | Industrie |
| Private Funders | MED-EL GmbH, Starnberg |
| Public Funders | |
| Sponsorship | |
| Cooperation Partners |
Project Finances
| Year | Amount Type | Sum | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fördersumme III (brutto mit PP) | 279,748.00 € |
Completed Projects
| Title | Optimierung der zeitlichen Verarbeitung bei CI-Hörgeräte-Versorgung, Teil 3 |
| Short Name | OCI III |
| Short Description | Das Nachfolgeprojekt von OCI II widmet sich der Entwicklung geeigneter Anpassungsmethoden zur Referenz-ITD-Reduktion bei bimodaler CI-Versorgung sowie deren Auswirkungen auf die Schalllokalisation. Es handelt sich um ein Projekt vom Typ IIT. Das Projekt ist mit einer kooperativen Promotion an der HS Offenburg verbunden. Die wissenschaftliche Fragestellung und die Methodenauswahl basieren auf eigenen Vorarbeiten, die an der Hochschule Offenburg in Kooperation mit der Uniklinik Freiburg erarbeitet und publiziert wurden. Ergebnisse, die innerhalb der Projekts erzielt werden, werden auf nationalen und internationalen Tagungen präsentiert und in einschlägigen nationalen und internationalen Fachjournalen publiziert. Journalartikel aus den Projekten OCI1 und OCI2 (Auszug): Zirn, S., Angermeier, J., Arndt, S., Aschendorff, A., & Wesarg, T. (2019). Reducing the device delay mismatch can improve sound localization in bimodal cochlear implant/hearing-aid users. Trends in Hearing, 23, https://doi.org/10.1177/2331216519843876. Angermeier, J., Hemmert, W., & Zirn, S. (2021). Sound Localization Bias and Error in Bimodal Listeners Improve Instantaneously When the Device Delay Mismatch Is Reduced. Trends in Hearing, 25, https://doi.org/10.1177/23312165211016165. |
| Year Of Acquisition | 2022 |
| Start Date | 2022-04-01 |
| End Date | 2025-03-01 |
| Project Managers | Zirn, Stefan, Prof. Dr. |
| Faculties | EMI |
| Institution | POIM |
| Funder Kind | Industrie |
| Private Funders | MED-EL GmbH, Starnberg |
| Public Funders | |
| Sponsorship | |
| Cooperation Partners |
Project Finances
| Year | Amount Type | Sum | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fördersumme III (brutto mit PP) | 279,748.00 € |